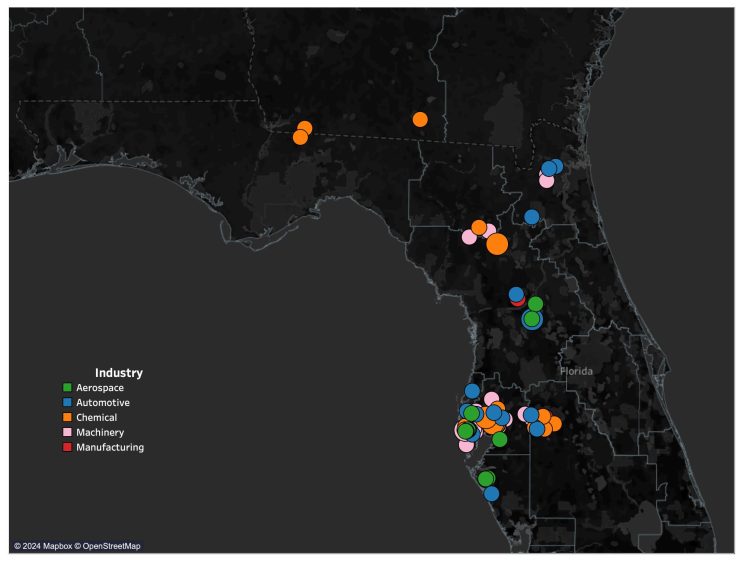
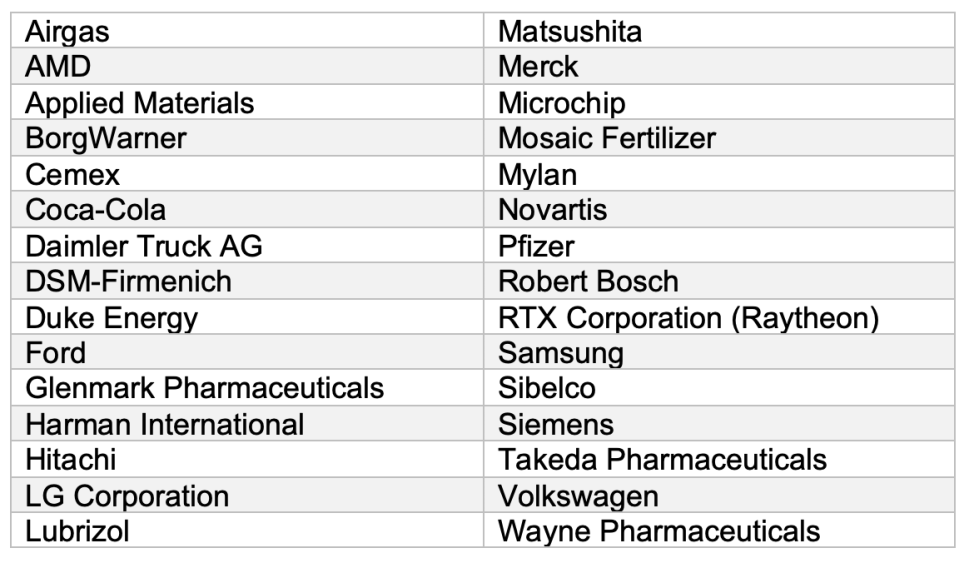
In recent months, the United States has aggressively pursued a protectionist trade strategy by introducing sweeping changes to its tariff policy—specifically targeting imported automobile components. Effective May 3, 2025, a flat 25% universal tariff will be imposed on all imported auto parts, in addition to existing country-specific duties. This marks a significant escalation in protectionist measures aimed at incentivizing domestic production and reducing reliance on foreign suppliers.
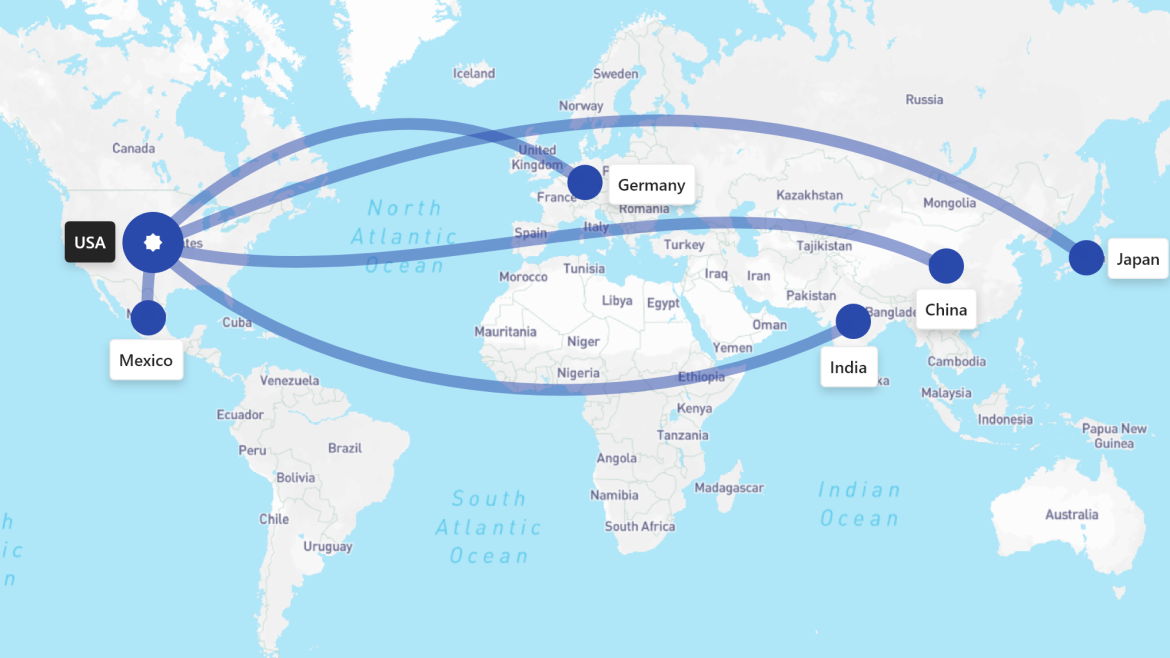
However, this shift poses significant operational and financial challenges for an industry that has long relied on global supply chains for efficiency and cost. Most major automobile manufacturers depend heavily on global sourcing: even vehicles assembled domestically often contain up to 70% of foreign-sourced parts. On average, 45% of vehicles sold in the U.S. are imported, with locally built vehicles also relying heavily on components from countries such as Mexico, China, Germany, India, and Japan—all now facing elevated tariffs.
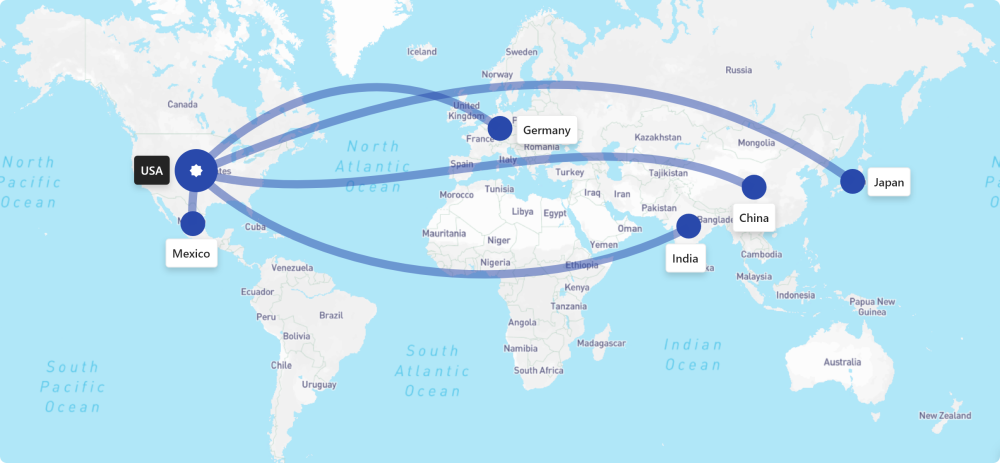
The new tariff framework does not replace existing duties; it adds on top of them, compounding their financial impact. Below is a snapshot of the effective tariff rates faced by key supplier countries:
| Country | Effective Tariff Rate | Notes |
| China | Up to 170% | Highest on record; multiple layers of tariffs applied |
| Germany, India, Japan | ~35% | 25% auto parts tariff + 10% universal tariff |
| Mexico | Up to 50% | 25% on non-USMCA goods + additional sectoral tariffs |
For manufacturers, these elevated rates directly increase input costs. For example, a component that previously cost $100 could now cost up to $270 if sourced from China—a staggering increase that ripples across the entire production budget.
Consider one of the Big Three American automakers operating one of their largest manufacturing facilities in the US. The plant produces a mix of SUVs and electric vehicles, relying heavily on components from Mexico, China, Germany, Japan, and the United States.
If the current cost for a mid-size SUV is around $45,000, approximately 57% of that cost comes from parts and raw materials. With about 70% of those components now exposed to higher tariffs, production costs could rise by approximately $5,000 per vehicle—even before factoring in additional inflationary pressures like tariffs on imported steel and aluminum.
This sharp increase in production costs could significantly impact the vehicle’s competitiveness in a crowded and price-sensitive market. Beyond a single facility or automaker, the consequences will be industry-wide:
- Consumer affordability could decline, leading buyers to seek alternatives with lower tariff exposure.
- Brand loyalty and market share could shift as buying patterns adjust to new cost dynamics.
- The automotive sector may face challenges in maintaining pricing strategies while adapting to these increased costs.
The following are potential strategies for manufacturers to mitigate the impact of these tariffs:
- Further diversify their supply chains: Explore alternative sourcing options outside high-tariff regions.
- Invest in domestic production: Increase manufacturing capacity in the U.S. to reduce reliance on imported components.
- Negotiate trade agreements: Engage with policymakers to advocate for favorable trade terms or exemptions.
Ready to Navigate the New Tariff Landscape?
Adapting to today’s rapidly evolving tariff structures can be complex and time-consuming. That’s why we created the U.S. Tariff Dashboard—a smarter way to assess risks, model costs, and make strategic decisions confidently.
With Adapt Ready’s platform, you can:
- Instantly Identify Your Supply Chain’s Weakest Links.
- Access Real-Time Tariff Data — No Manual Research Needed.
- Simulate “What-If” Scenarios for Smarter Budgeting.
- Discover Lower-Cost Alternative Suppliers in Minutes
- Benchmark Your Exposure Against Industry Peers
Update — April 29, 2025:
Following an executive order by President Trump, key adjustments were made to soften the impact of the auto parts tariffs. Notably:
- Tariff stacking is restricted: The 25% auto parts tariff will not be compounded with existing steel, aluminum, or USMCA-related duties.
- Tariff credits apply to U.S.-assembled vehicles: Automakers assembling cars in the U.S. with ≥85% domestic/USMCA content can receive credits up to 3.75% of MSRP in the first year, tapering to 2.5% in year two.
- Implication: Manufacturers producing vehicles domestically may partially offset increased costs, improving resilience and competitiveness.
While this executive order offers short-term relief, challenges remain for companies with global sourcing models and non-U.S. production bases. Strategic supply chain diversification and domestic investment are still critical.